Kubernetes has become a cornerstone in modern IT environments, significantly revolutionizing the way applications are deployed and managed. Its ability to automate scaling, deployment, and management of containerized applications makes it indispensable for businesses aiming for agility, scalability, and efficiency. As organizations increasingly adopt microservices architectures, Kubernetes’ role in providing seamless orchestration and robust security continues to grow in importance.
However, along with its benefits, Kubernetes introduces complexity and challenges in managing vulnerabilities. Understanding and addressing these challenges is crucial for maximizing the advantages Kubernetes offers while maintaining robust security.
The Kubernetes Complexity Paradox: Complex and Easier
Kubernetes brings a paradox: it simplifies many aspects of application deployment and management but also introduces new layers of complexity, particularly in vulnerability management. Let’s explore some key challenges:
- Scalability and Dynamic Infrastructure: Kubernetes’ ability to scale dynamically means a single vulnerability can have massive exposure. The vast number of containers running across clusters can make identifying and evaluating the risk criticality of vulnerabilities difficult.
- CI/CD and Automation: Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) pipelines automate code deployment, potentially allowing vulnerabilities to enter the system unnoticed. The speed and frequency of deployments when using Kubernetes can make it difficult to track and remediate vulnerabilities quickly.
- Communication Between Containers: Communication both within the Kubernetes cluster and between the cluster and external systems can be largely unprotected. An exploited vulnerability in one container can have a significant blast radius, affecting other services within the cluster as well as external systems that communicate with it. This communications complexity can increase the potential impact of vulnerabilities, making it essential to implement robust security measures.
Despite these challenges, and this complexity paradox, Kubernetes also offers tools and features that can be used to significantly enhance and simplify vulnerability management.
How Kubernetes Can Help Improve and Simplify Vulnerability Management
Kubernetes, despite its complexity, offers enhanced visibility, easier access to information, a layered network policy model, and numerous additional features that improve and streamline vulnerability management processes. Let’s delve into how Kubernetes can simplify vulnerability management:
100% Inventory
Kubernetes provides a comprehensive inventory of every containerized application within a cluster. This complete visibility ensures that no assets are missing, eliminating the need to spend time and resources searching for hidden or overlooked components. Knowing exactly what is running in your environment is one of the most important tasks in effective vulnerability management.
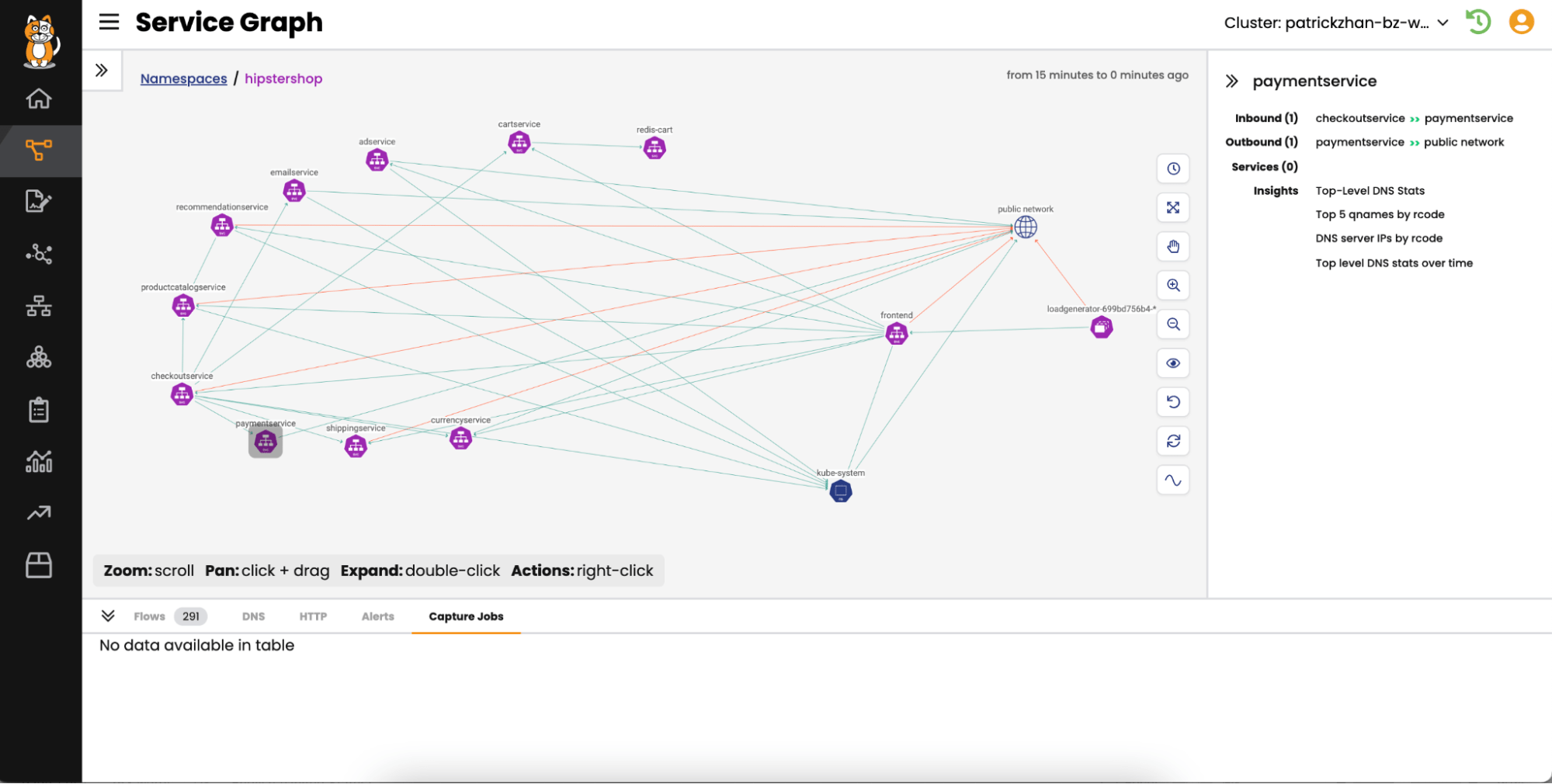
Image-Based Vulnerability Management
Kubernetes’ reliance on container images simplifies vulnerability management from a shift-left perspective. By tightly coupling vulnerability scanning with the CI/CD pipeline, vulnerabilities can be detected and addressed before deployment. This proactive approach helps prevent vulnerable code from entering the production environment, enhancing overall security. Vulnerability management tools can also show you which images contain vulnerabilities referenced by a CVE (CVE-to-Image). They can also look at a CVE in an image and tell you all of the cluster nodes that are affected (i.e. which cluster nodes use that image).
In addition, Kubernetes features an admission controller for image assurance, acting as a gatekeeper to block the deployment of images with known vulnerabilities. Image deployment rules, which are also called guardrails, are fully configurable.
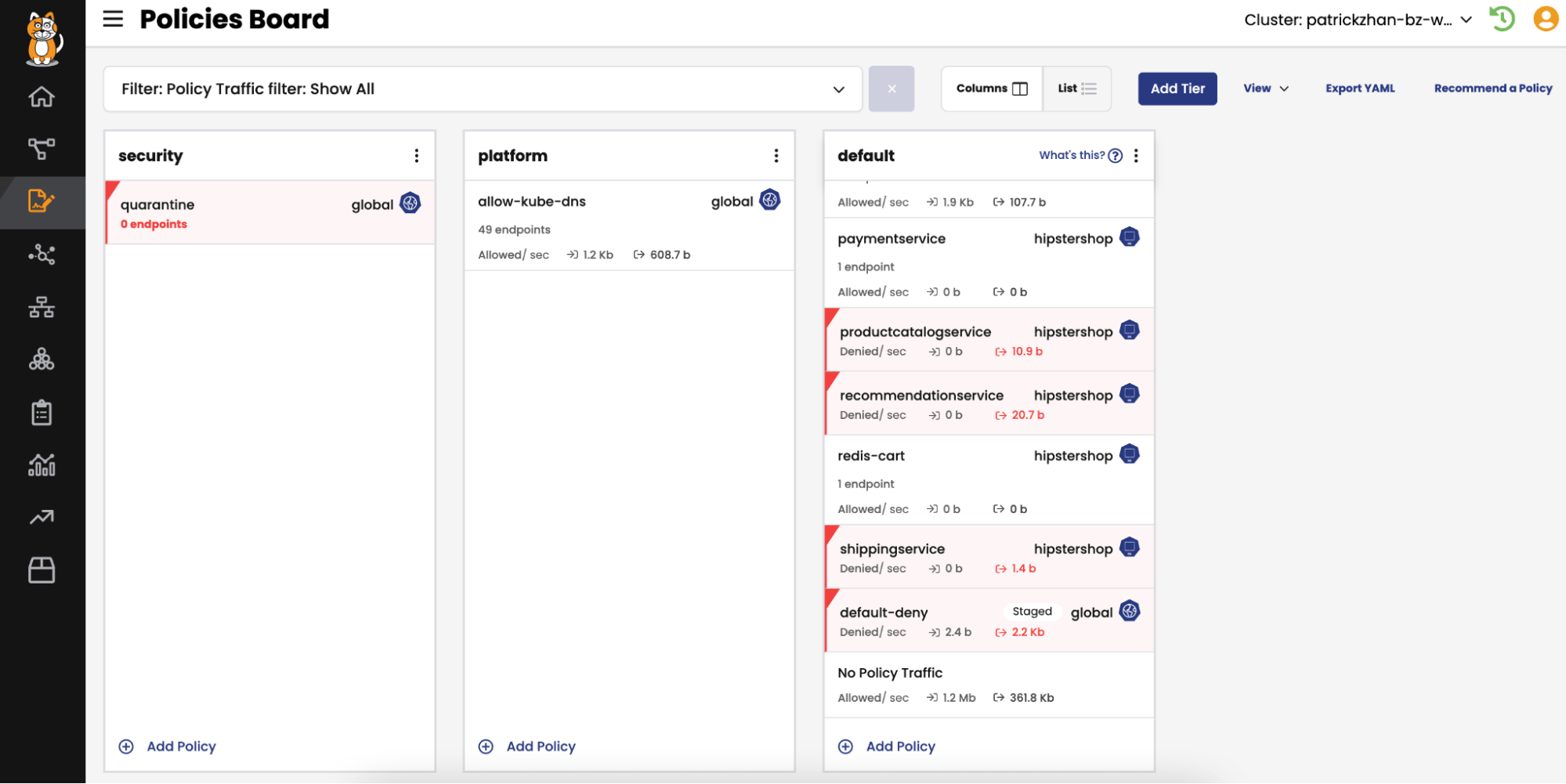
Isolation with Namespaces and Network Policies
Kubernetes namespaces and network policies facilitate the isolation of components, which are powerful capabilities for mitigating vulnerabilities. By segmenting applications and enforcing network policies, Kubernetes limits the potential impact of vulnerabilities. The flexible isolation that Kubernetes provides makes it easier to manage and contain vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of widespread exploitation.
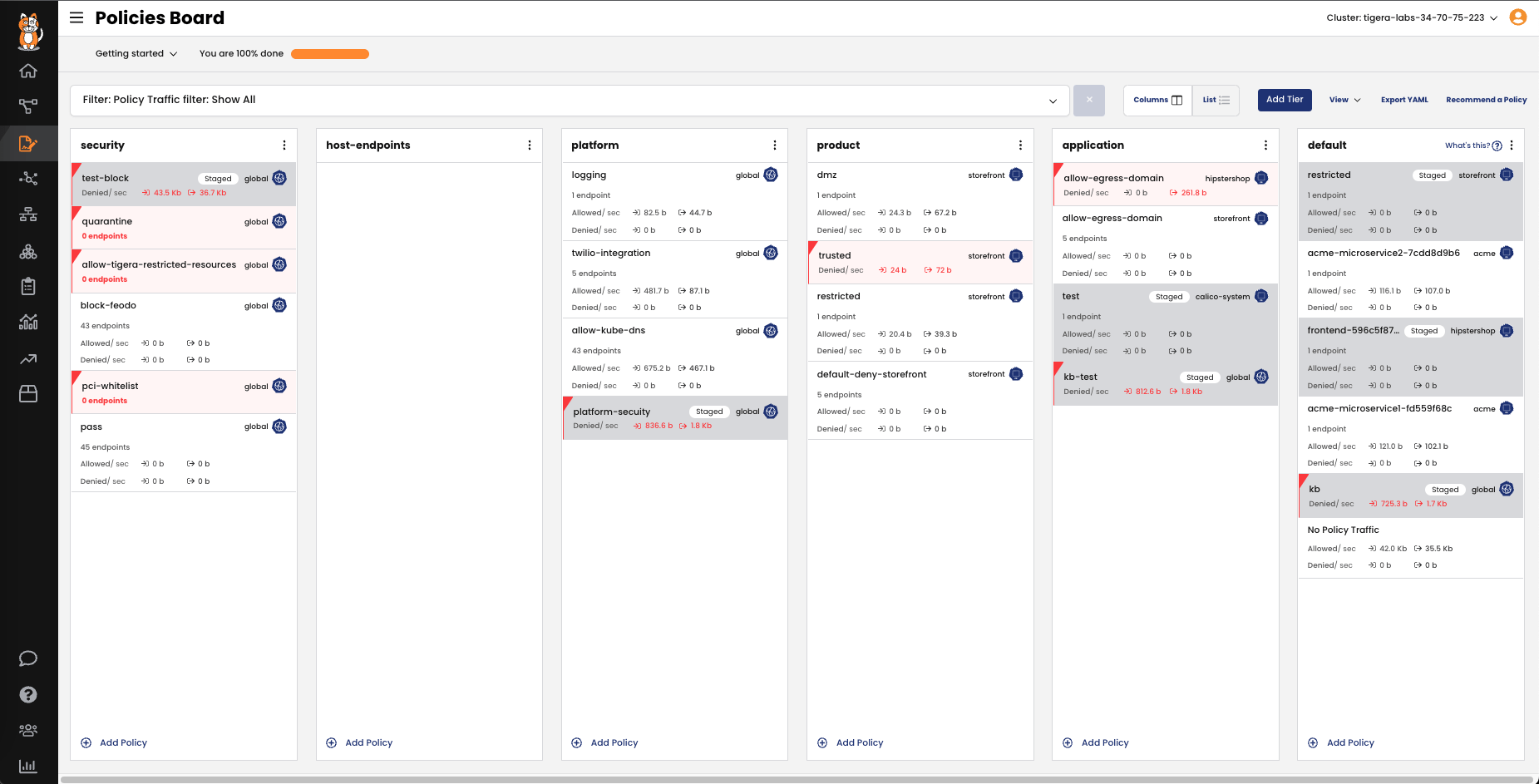
Modular Network Policies
Kubernetes offers a layered network policy model that enhances visibility and control over network traffic. These policies allow administrators to define and enforce rules for communication between containers and services. By monitoring and restricting network connections, Kubernetes helps prevent unauthorized access and limits the spread of vulnerabilities.
Kubernetes network policies support continuous vulnerability management by providing the ability to quarantine high-risk workloads and mitigate vulnerabilities. This approach ensures rapid response to threats while minimizing operational impact.
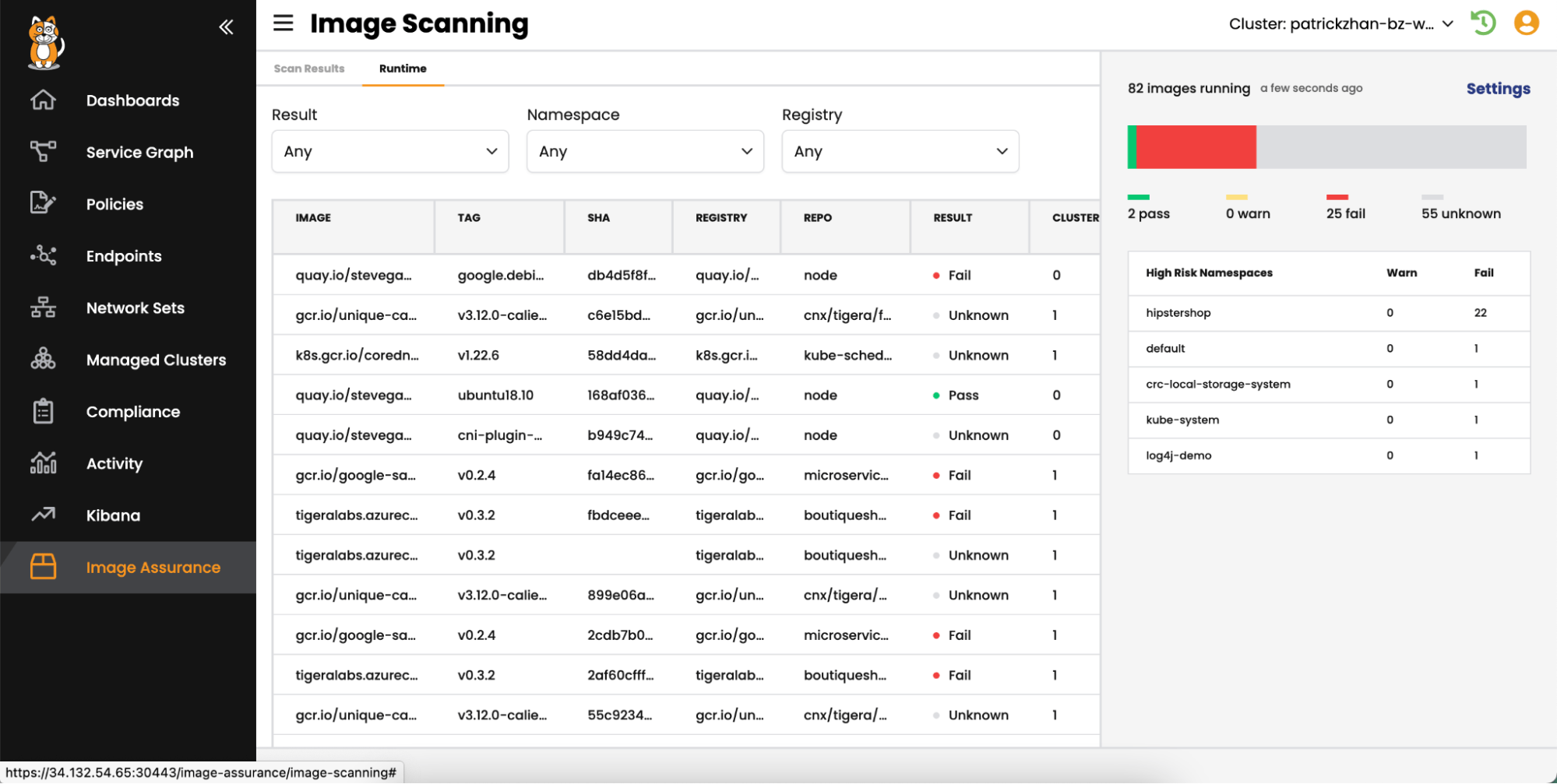
In-Cluster Vulnerability Scanning
Kubernetes can provide precise visibility into the source of images used to create nodes in your cluster. This eliminates guesswork when conducting in-cluster vulnerability scans, offering exact details about which image (and its location) contains the identified vulnerability.
Rich Information and Observability
Kubernetes centralizes a wealth of information (information on the control plane and information about container workloads) that aids in vulnerability management. This includes inventory data, configuration settings, networking policies, audit logs, and access control information (RBAC). The availability of this rich data enables security teams to make informed decisions, quickly identify vulnerabilities, and assess risks accurately. The comprehensive observability provided by Kubernetes helps ensure that critical information is not overlooked.
Simplified Updates and Remediation
Keeping Kubernetes and its components up to date is essential for security. Kubernetes simplifies the update process through automated updates and rolling deployment capabilities, ensuring that vulnerabilities in the Kubernetes environment itself are promptly addressed. This ease of updating extends to the containers running within the cluster, making the remediation process more efficient and reducing vulnerability exposure windows.
Conclusion
Kubernetes, while inherently complex, provides powerful features that can significantly simplify vulnerability management. Its capabilities include a comprehensive inventory of containerized applications, integration with CI/CD pipelines for proactive vulnerability scanning, isolation mechanisms through namespaces and network policies, and more. By leveraging these features, organizations can enhance their vulnerability management practices, making their security efforts more effective and efficient. Embrace Kubernetes not only for its scalability and automation but also for its potential to transform and simplify the way you manage vulnerabilities.
For more information on leveraging vulnerability management on Kubernetes, and to learn more about Calico, please visit the Calico Vulnerability Management product page.
Related Guides:
- Kubernetes Security: 8 Best Practices to Secure Your Cluster
- Kubernetes Networking: The Complete Guide
- Microsegmentation Security: The Evolution of Cybersecurity in a Zero Trust World
Related Products:
