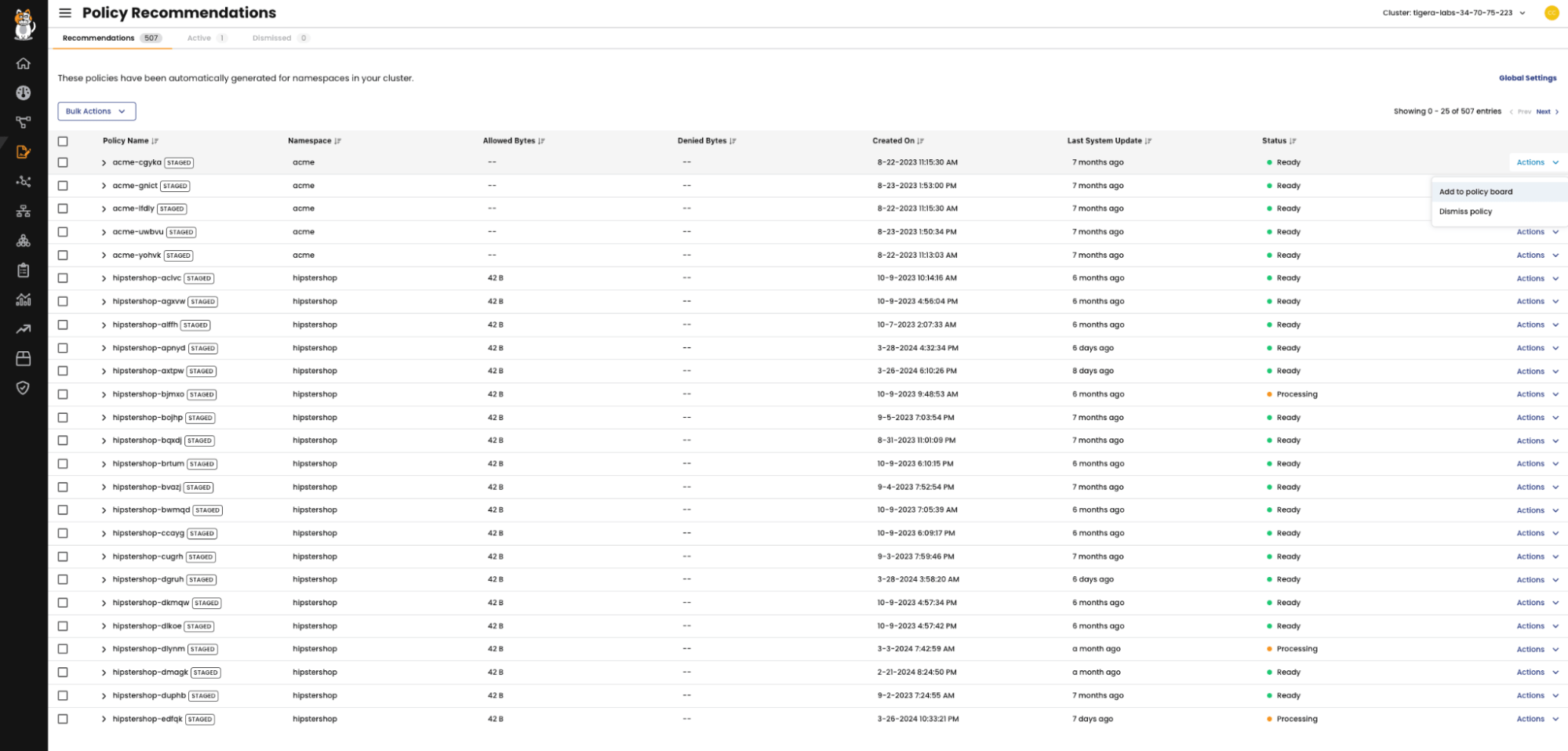
Microsegmentation represents a transformative approach to enhancing network security within Kubernetes environments. This technique divides networks into smaller, isolated segments, allowing for granular control over traffic flow and significantly bolstering security posture. At its core, microsegmentation leverages Kubernetes network policies to isolate workloads, applications, namespaces, and entire clusters, tailoring security measures to specific organizational needs and compliance requirements.
The essence of microsegmentation strategies
Scalability and flexibility
The fundamental advantage of microsegmentation through network policies lies in its scalability and flexibility. Kubernetes’ dynamic, label-based selection process facilitates the addition of new segments without compromising existing network infrastructure, enabling organizations to adapt to evolving security landscapes seamlessly.
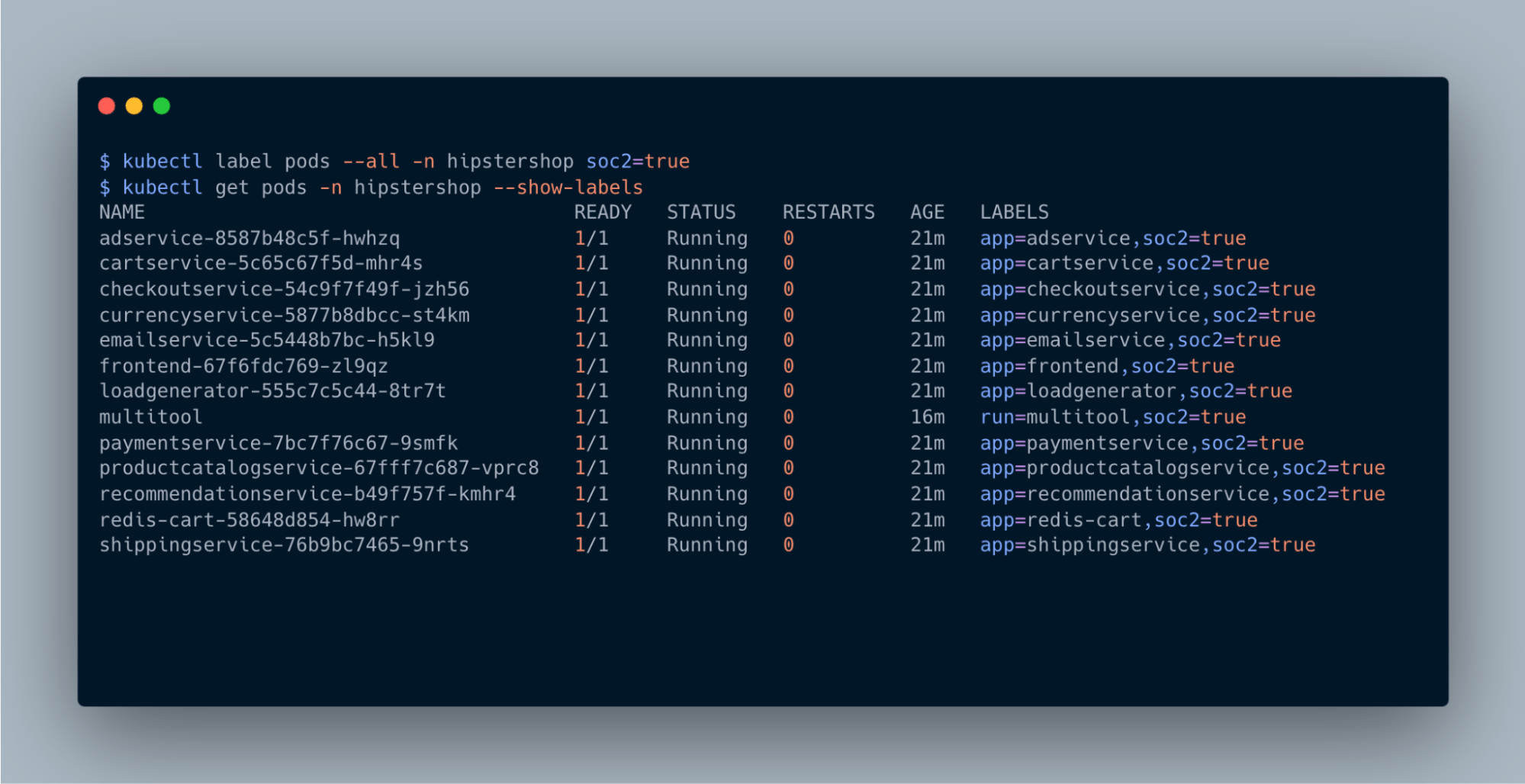
Prevent lateral movement of threats
Workload isolation, a critical component of microsegmentation, emphasizes the importance of securing individual microservices within a namespace or tenant by allowing only required and approved communication. This minimizes the attack surface and prevents unauthorized lateral movement.
Namespace and tenant isolation
Namespace isolation further enhances security by segregating applications into unique namespaces, ensuring operational independence and reducing the impact of potential security breaches. Similarly, tenant isolation addresses the needs of multi-tenant environments by securing shared Kubernetes infrastructure, thus protecting tenants from each other and mitigating risks associated with infrastructure-level attacks.
Implementing microsegmentation in Kubernetes
Implementing microsegmentation involves several key steps, starting with the identification of security domains and the definition of a policy model that reflects the specific communication patterns within those domains. Domains can be organizational, workload-type, or regional.
This approach makes sure that only traffic that is specifically allowed can go through the network as defined in domains by enforcing a “default deny” stance, which means that all traffic is blocked unless it’s explicitly permitted.
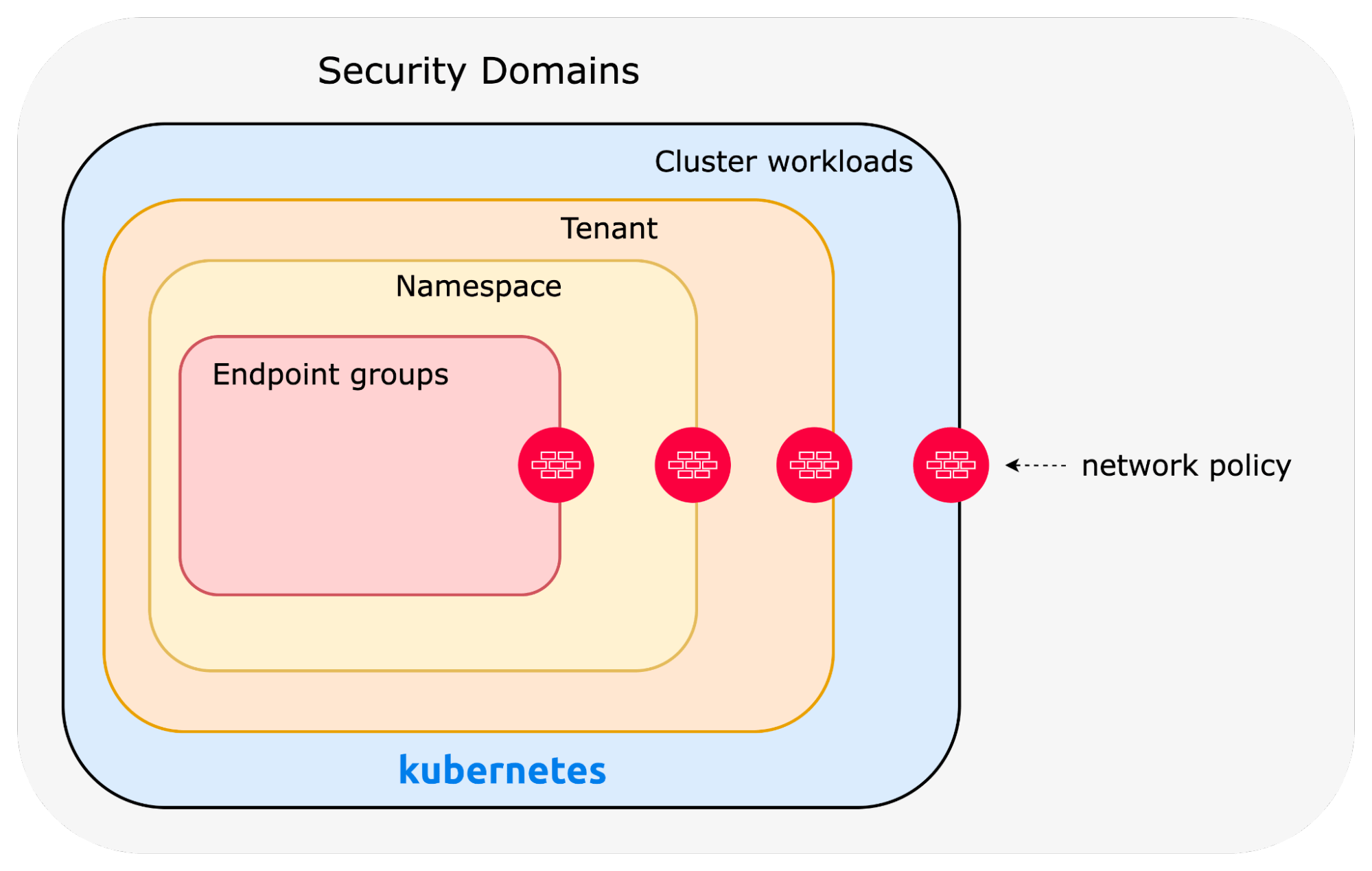
Here are a few tips for accelerating microsegmentation deployment in Kubernetes clusters:
- Identify endpoints: Automatically detect network identities (IP) for pods and nodes that fall into the standard Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) public and private network designations, and display those as entities on a graph.
- Advanced policy authoring: Provide policy ordering/priority, deny rules, and more flexible match rules, extending policies beyond pods to VMs and host interfaces.
- Ecosystem extensibility: Support securing applications at layers 5-7, offering match criteria based on workload identity.
- Policy enforcement within organizational guardrails: Allow organizations to enforce high-precedence policies that are non-negotiable for enterprise security. This ensures critical frameworks such as NIST, GDPR, PCI, and SOC 2 are always adhered to and provides a hierarchy to traffic flow execution.
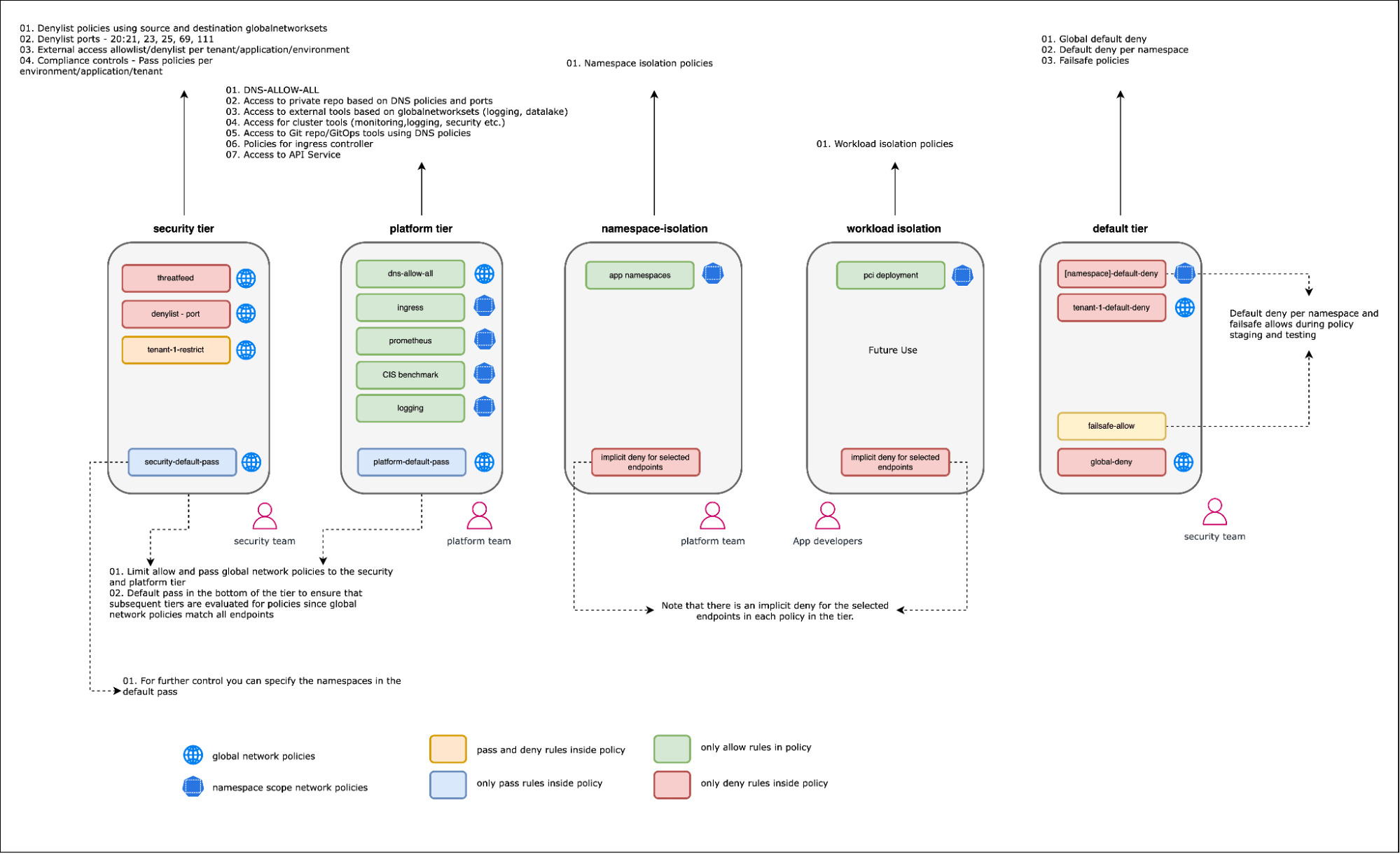
- Policy recommendations: Use specialized technologies like Calico that provide automatic workload isolation, thus simplifying the creation and enforcement of effective network security policies.
- Declarative microsegmentation: Deploy microsegmentation as code, allowing administrators to define security intentions in YAML or through the UI and apply them based on workload identity using label selectors.
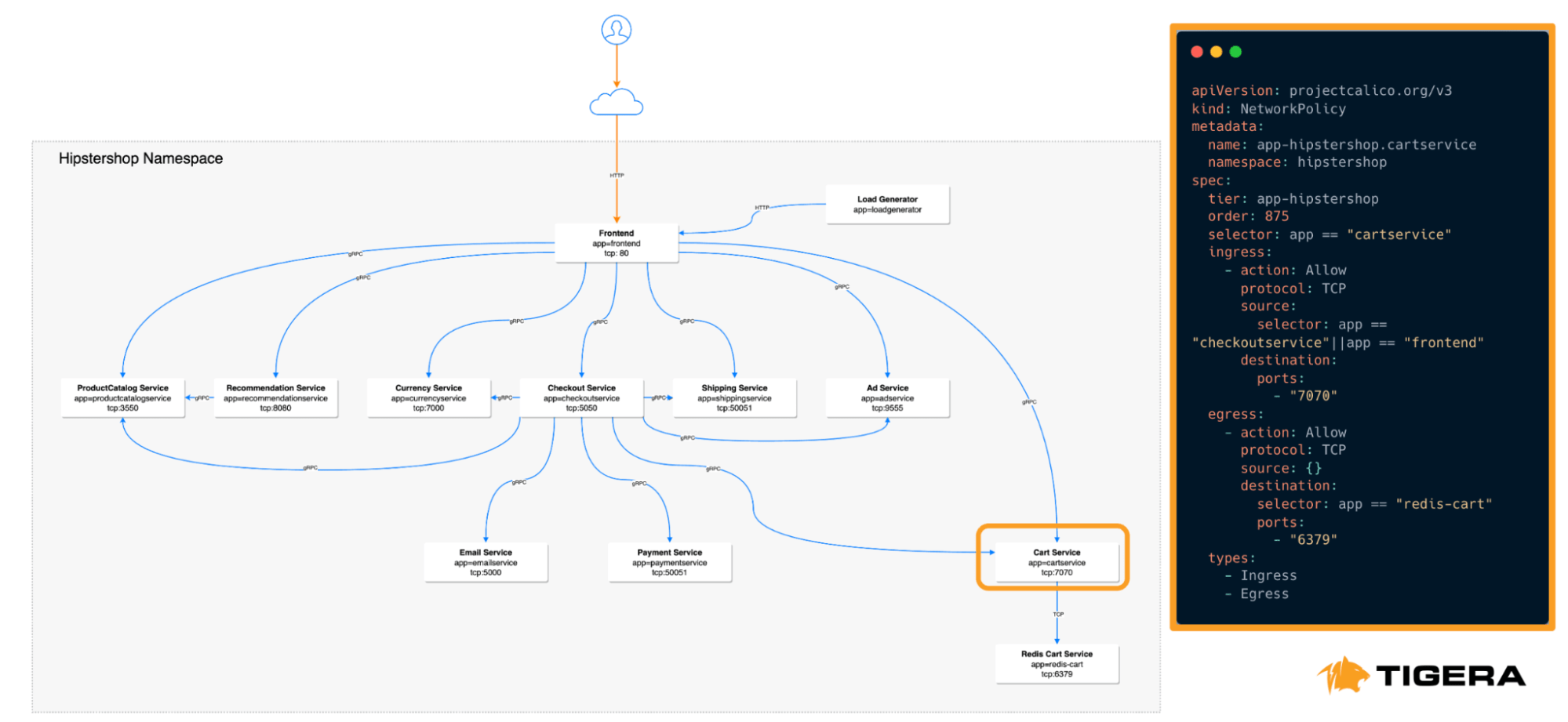
- Dynamic microsegmentation: Dynamically segment workloads based on their identities, such as labels, namespaces, and service accounts, enhancing security and flexibility.
Benefits and impact
- Improved security posture: Enabling more granular, flexible, and dynamic microsegmentation can help organizations better protect their Kubernetes environments against threats.
- Operational efficiency: The hierarchical policy management and UI tools simplify the management of complex policy structures for microsegmentation, making it easier for teams to implement and maintain security policies.
- Compliance and risk management: Advanced policy management capabilities help in meeting compliance requirements and managing risks more effectively, by ensuring that only authorized traffic is allowed and potentially harmful traffic is blocked.
- Reduced infrastructure cost: By using microsegmentation, organizations can create multi-tenant Kubernetes clusters to leverage the same underlying infrastructure resources while keeping tenant isolation in place.
Conclusion
Ultimately, microsegmentation with Kubernetes and Calico represents a strategic approach to network security, offering scalable, flexible, and precise control over network traffic. By implementing microsegmentation, organizations can significantly enhance their security posture, protect critical workloads, and meet stringent compliance requirements, all while maintaining the agility and scalability essential in modern cloud-native environments.
To get started with microsegmentation, complete our 30-min self-paced workshop
Join our mailing list
Get updates on blog posts, workshops, certification programs, new releases, and more!